Page 214 - EN_final
P. 214
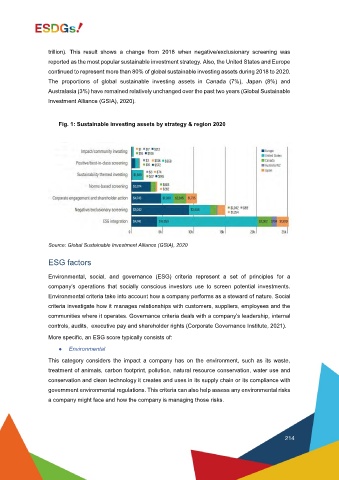
trillion). This result shows a change from 2018 when negative/exclusionary screening was
reported as the most popular sustainable investment strategy. Also, the United States and Europe
continued to represent more than 80% of global sustainable investing assets during 2018 to 2020.
The proportions of global sustainable investing assets in Canada (7%), Japan (8%) and
Australasia (3%) have remained relatively unchanged over the past two years (Global Sustainable
Investment Alliance (GSIA), 2020).
Fig. 1: Sustainable investing assets by strategy & region 2020
Source: Global Sustainable Investment Alliance (GSIA), 2020
ESG factors
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria represent a set of principles for a
company’s operations that socially conscious investors use to screen potential investments.
Environmental criteria take into account how a company performs as a steward of nature. Social
criteria investigate how it manages relationships with customers, suppliers, employees and the
communities where it operates. Governance criteria deals with a company’s leadership, internal
controls, audits, executive pay and shareholder rights (Corporate Governance Institute, 2021).
More specific, an ESG score typically consists of:
● Environmental
This category considers the impact a company has on the environment, such as its waste,
treatment of animals, carbon footprint, pollution, natural resource conservation, water use and
conservation and clean technology it creates and uses in its supply chain or its compliance with
government environmental regulations. This criteria can also help assess any environmental risks
a company might face and how the company is managing those risks.
4
214
214